Aggregates
Aggregate Columns provide a mechanism for analyzing data in summary from across one or more tables. This section gives an overview of aggregate creation in Engine but it is worth noting that the Campaign Manager Help section covers specifics of creating aggregates in the application.
With aggregate functions, it is possible to determine values such as the number of people in a family, the total transaction value for a customer, the number of purchases made for a particular geographic region or the first Order Date for a specific customer.
In order to create an aggregate, a relationship is required between 2 tables - either as a direct link between the tables, or as an indirect link via intermediary tables.
The simplest form of aggregation is a COUNT, which can be created by specifying two table names, i.e. Count of Customers in each Household. All other aggregations require a numeric field as input for the function column, where the function column is the column summarized in the aggregation i.e. Last Purchase date using Purchase Date on the Order table, summarized to a Customer table to provide a single date for each Customer.
Rules for creating Aggregates
As for any field within Engine, an aggregate field must be created on a table. This table is referred to as the Resolution or Owner Table of the aggregate and must be on the ONE side of a [ONE to MANY] join.
The function column - the column that is going to be summarized - always comes from the MANY side of a [ONE to MANY] link.
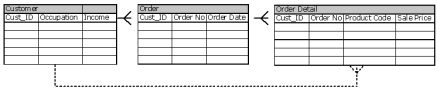
In the data structure below, it is possible to create aggregates on the CUSTOMER or ORDER tables, but not on the ORDER DETAIL table.
The following aggregate fields could be created given the data structure provided;
| Name | Resolution Table | Function Column | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Sales | Customer | [Order Details].[Sales Price] | SUM |
| First Order Date | Customer | [Order].[Order Date] | MIN |
| Total Orders | Customer | [Order].[Order No] | COUNT |
| Item Count | Order | [Order Detail].[Cust_ID] | COUNT |
Types of Aggregate
The following table lists the type of aggregate fields that can be created.
| Aggregate Type | Description | Function Column |
|---|---|---|
| COUNT | Returns the count of Non-Null values for the specified function column. | ANY |
| MIN | Returns the minimum value for the specified function column. | Numeric, Date, DateTime, Time |
| MEAN | Returns the average integer value for the specified function column, where average = SUM/COUNT | Numeric |
| MAX | Returns the maximum value for the specified function column. Function column can be Numeric, Date, DateTime or Time. | Numeric, Date, DateTime, Time |
| RMEAN | Returns the average real value for the specified function column, where average = SUM/COUNT | Numeric |
| SUM | Returns the sum of non-null values for the specified function column | Numeric |
| STANDARD DEVIATION | The standard deviation for the specified function column within the population (i.e. distance from MEAN value) | Numeric |
| SUM OF SQUARES | The sum of all the squares of the individual values in the function column | Numeric |
Operational Elements of an Aggregate
| Dynamic Field | Owner Table | Table on which the aggregate is created. |
|---|---|---|
| Function Column | Column that is summarized by the aggregate. Column must come from the same table as the Owner Table or from the MANY side of a link. | |
| Source Table | The owner table(s) of the Function column. | |
| Having Field(s) | Fields used in the having clause of the aggregate. Must be linked to the Owner Table of the aggregate. |